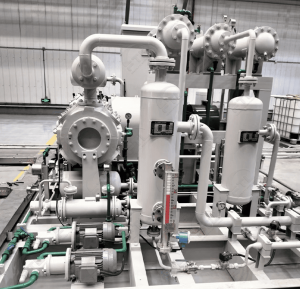
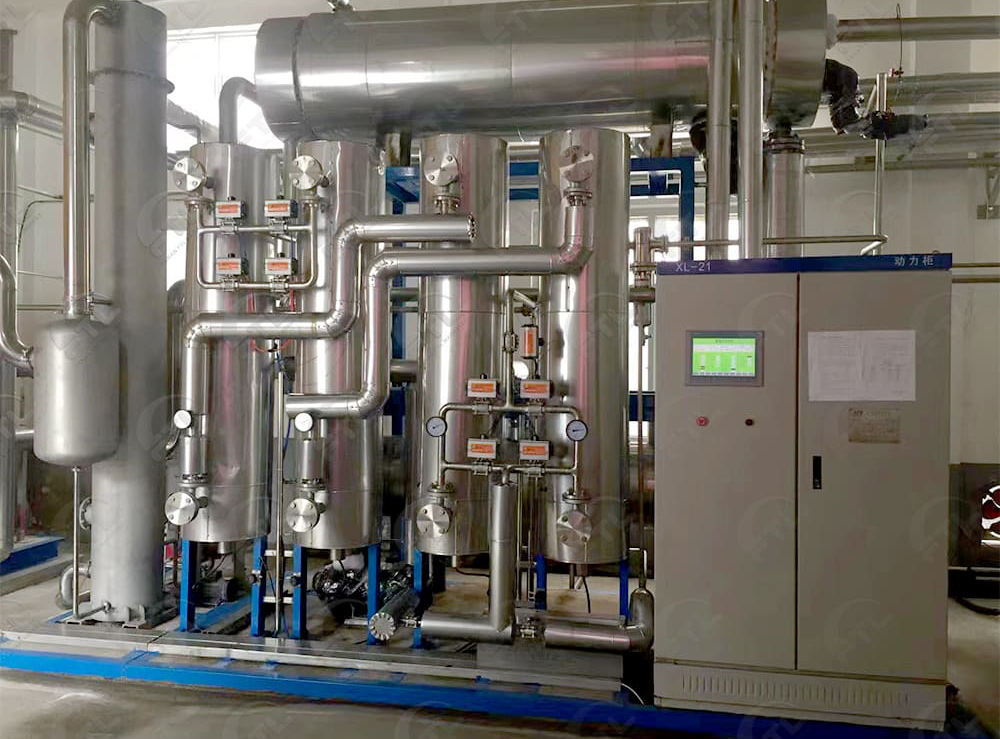
It mainly processes low-pressure, high-CO₂-concentration gas sources (such as lime kiln gas, flue gas, and fermentation tail gas). The CO₂ concentration is increased from 8–13% to ≥95%, with a recovery rate of 70–90%.
CO2 product details



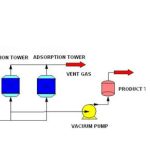
PSA separation
Pressure Swing Adsorption
Product Overview
- Mature process, simple operation, and stable operation.
- High-purity CO₂ product and high recovery rate.
- Low energy consumption and good economic efficiency.
- Fully automatic control with remote monitoring capability.
- Adapts to fluctuations in gas volume and composition, enabling flexible operation.
The selectivity of the adsorbent and pressure changes
Adsorption Stage (High Pressure):
When a mixed gas stream is fed into an adsorption tower containing adsorbent under high pressure, the adsorbent preferentially adsorbs one or several specific components.
For example, in nitrogen production, carbon molecular sieves exhibit stronger adsorption capacity for oxygen and carbon dioxide than for nitrogen. Consequently, under high pressure, oxygen and carbon dioxide are captured by the adsorbent, while nitrogen escapes as the non-adsorbed component, yielding a high-purity nitrogen product.
Desorption Stage (Low Pressure):
Once the adsorbent reaches saturation, gas flow is halted. Pressure reduction (typically to atmospheric pressure or vacuum) releases the adsorbed components from the adsorbent.
As pressure decreases, the adsorbent's adsorption capacity weakens. Previously adsorbed gases like oxygen and carbon dioxide are “released,” regenerating the adsorbent for the next adsorption cycle.
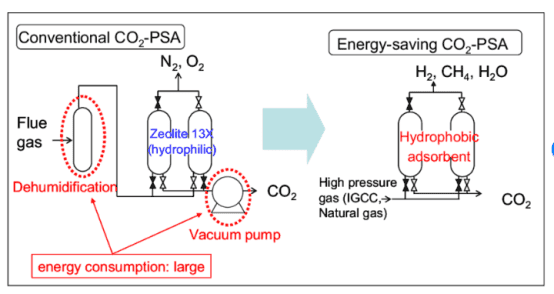
Related Products