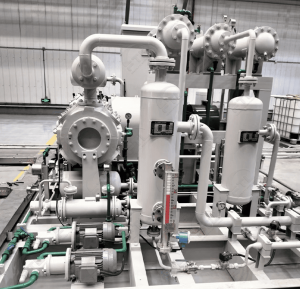
It enables the reaction between organic compounds in tail gas and oxygen at a relatively low temperature through the action of a catalyst, thereby concentrating and separating CO₂. It is suitable for treating low-concentration CO₂ waste gas in industries such as chemical engineering, metallurgy, and electric power.
CO2 product details





Catalytic combustion method
Catalytic Oxidation
Product Overview
- Low-temperature & High-efficiency: The reaction is completed at 250–400℃, with low energy consumption.
- Environmental Protection & Cleanliness: Reduces secondary pollutants such as NOₓ.
- Stability & Durability: The catalyst has a long service life, suitable for continuous operation.
- Wide Application: Capable of treating various types of industrial tail gas.
Catalytic Combustion
Preheating:
Waste gas containing organic compounds is first directed into a heat exchanger for preheating. If the exhaust gas concentration is low, an additional heat source (such as electric heating or gas combustion) is required to raise its temperature to the initial threshold needed for catalytic reaction.
Catalytic oxidation:
The preheated exhaust gas enters the catalytic bed equipped with a catalyst. On the surface of the catalyst, organic molecules undergo chemical adsorption and reactions with oxygen molecules. These organic substances are oxidized and decomposed to produce CO2 and H2O. This process will release a large amount of heat, causing the gas temperature to rise.
Heat recovery:
The high-temperature purified gas exits the reaction zone into a heat exchanger, transferring its heat to the untreated cold exhaust gas. This achieves heat recovery, reducing system energy consumption and enabling the entire unit to operate in **“self-heating mode”** when exhaust concentrations reach a certain threshold—maintaining the reaction without additional heating.
Related Products